Shadow IT is an old danger taking many new forms in companies today. Specifically, Shadow IT systems and solutions built inside organizations without explicit approval. For example, when someone sets up a DropBox account to share internal files, or when someone saves information on a flash drive and takes it home with them, this puts your company’s information at risk. These are real dangers that happen all of the time and are frequently missed, even by IT, as no one can monitor everything in an organization.
Application or transmission of data without authorization by IT increases the odds of unofficial, uncontrolled data flows through online messaging software, email services, document sharing software, and portable data storage devices. This makes it difficult for organizations to comply with standards such as international standards for banking (BASE II), Total Quality Management (TQM), and the Health Insurance Portability Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Shadow IT is a bit more prevalent in small companies that tend to have fewer restrictions and policies. And while larger firms may have more restrictions, these are easy to circumvent due to; distributed IT, multiple sites, and siloed business operations. Big organizations face the greatest challenge as more departments with sufficient budgets deploy the technology on their subnetwork or network.
Not every Shadow IT operation is intentional. Some employees may use software that is more familiar to them or more efficient than what is already in place, without checking whether it adheres to companies’ security and compliance policies.
For this reason, the proper security guidelines and acceptable use policies must be in place to protect the business when any form of Shadow IT occurs. Failure to comply with security, documentation, and reliability standards obviously poses several problems.
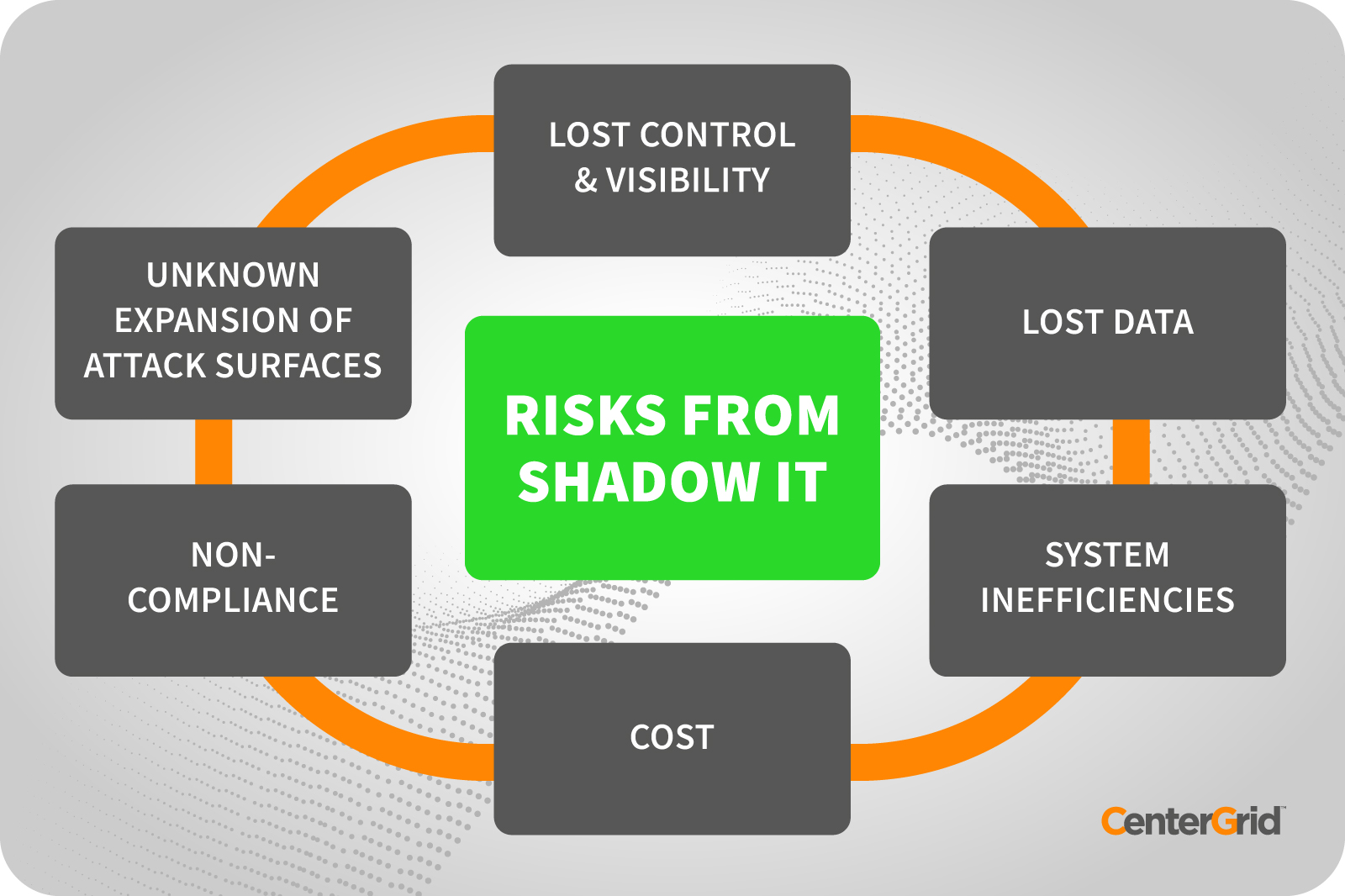
The Dangers of Shadow IT
Data loss or leaks
Contractors or personnel in Shadow IT operations may never be vetted or adequately educated on proper data handling, which may lead them to share sensitive data with unauthorized people. This is made worse because they don’t back up data in case it is lost or compromised. When staff leaves an organization, they often take proprietary data, which is a huge risk for organizations.
Inconsistency and Duplicate Content
Shadow IT can cause poor arrangement and flow of linked files which has the power to distort analysis methodology. Shadow systems will likely cause inconsistencies in a company’s data and logic. Inconsistent results would arise from differences between shadow files and those in proper locations. Errors are often not easily detected owing to a lack of version control and rigorous testing.
Wasted time and resources
Without the required experience, personnel spends lots of time discussing or re-checking data validity, setting up systems, and managing different software and data versions. Besides time, Shadow IT carries a huge risk of resource wastage as unauthorized applications are stored on company resources. Unapproved applications often prevent full return on investment and leave vulnerabilities in place. This type of Shadow IT prevents management from correctly anticipating costs when trying to deliver products and solutions.
Security
The biggest risk associated with Shadow IT is security. Removable disks, cloud, and other potential shadow platforms used by employees may not be as secure as the IT department would like. It is easy for attackers to infect the entire system with viruses, malware, and ransomware which cause everything from monetary loss to data loss.
Prevention and Protection of Shadow IT
There is very little an IT team can do to protect an organization where Shadow IT is the norm. As such, company rules must be the first tool implemented in protecting its assets.
Companies that are unable to protect their digital assets or rein in rogue applications need to take the time to audit their environments and understand all risks present. Knowing this, an organization should consider the following tactics to address Shadow IT Internally:
- Start with educating your employees on what is acceptable data use and what is not permitted in your organization.
- Have a professional audit of the security of your environment. When done properly, you will have a detailed picture of the security of each area of your business.
- Review each department’s finances by auditing and reviewing all unknown software and potential data access risks line items.
- Consider prohibiting the exchange of data between cloud and internal applications without approval by IT.
- Implement functionality controls at an IP level to restrict unauthorized downloading, uploading, or posting of company data.
Data loss prevention (DLP) software can also help to recognize and restrict the transfer of sensitive data, whether intentional or otherwise.
Finally, as always with data, have a solid disaster recovery plan in place when facing the loss of or access to company data.
A combination of practices is needed to blunt the risks of Shadow IT without adversely affecting business operations. Understanding the risks gives organizations a chance of staying safe in this era of complex security challenges.
If you need more information on this and other IT issues, contact us. We are professionals who will listen to your needs and provide the best solutions or answers to ensure smooth, secure business operations.
